BALLISTIC GALVANOMETER By Labcare Export
Price 5400.0 INR/ Piece
BALLISTIC GALVANOMETER By Labcare Export Specification
- Voltage
- Operates at Small Potential Differences (Millivolt Range; Not for High Voltage)
- Temperature Range
- Room Temperature (Typically 10C to 40C)
- Frequency
- DC (Direct Current) Only
- Power Source
- External Source (Passive Instrument)
- Capacity
- Not Applicable (Reflects charge sensitivity, not load)
- Automation Grade
- Manual Operation
- Feature
- High Sensitivity, Low Damping, Mirror & Lamp Scale Arrangement, Zero Adjuster
- Model No
- LBG-101 (or As per Company Catalog)
- Measurement Range
- 10 micro-coulombs to 200 micro-coulombs (varies by setup)
- Core Components
- Moving Coil, Suspension Fiber, Scale, Mirror, Damping Magnet, Glass Case
- Accuracy
- High Sensitivity; Deflection Typically Proportional to Charge (micro-coulombs scale)
- Equipment Materials
- Heavy Cast Iron Base, Non-Magnetic Frame, Glass Front, Brass Fittings
- Type
- Moving Coil, Mirror Type
- Usage
- Measurement of electric charge/discharge in physics labs, educational demonstrations
- Display Type
- Analog (Deflection Scale)
- Dimension (L*W*H)
- Approx 18 cm x 12 cm x 20 cm
- Weight
- Approx 1.5 - 2.0 kg
- Mirror Arrangement
- Plane Mirror for Lamp & Scale/Spot Reflection Method
- Connection Terminals
- Brass Terminals with Knurled Nuts
- Finish
- Durable Enamel Paint/Coating for Rugged Use
- Operating Principle
- Faradays Law of Electromagnetic Induction
- Internal Resistance
- Approx 500 2000 Ohms
- Suspension
- Phosphor Bronze Ribbon or Quartz Fiber
- Damping
- Air Damping with Soft Iron Cylinder and/or Magnetic Damping
- Scale Graduation
- Mirror Scale, Anti-Parallax with Fine Markings
- Deflection Type
- Ballistic (Proportional to Quantity of Charge)
- Package Contents
- Instrument, Operation Manual, Standard Accessories
- Pointer Type
- Knife Edge, Anti-Static
BALLISTIC GALVANOMETER By Labcare Export Trade Information
- Minimum Order Quantity
- 1 Piece
- Supply Ability
- 100 Pieces Per Week
- Delivery Time
- 7 Days
- Sample Available
- No
- Main Domestic Market
- [, ', A, l, l, , I, i, a, ', ], n, d
About BALLISTIC GALVANOMETER By Labcare Export
A Ballistic Galvanometer is a highly sensitive device used for measuring the charge or current produced during a brief electric pulse, often in research and laboratory settings. It operates on the principle of electromagnetic induction, where the moving coil is deflected by the current passed through it, which is proportional to the magnitude of the pulse. The deflection is recorded, providing information about the electric charge or impulse duration. It is particularly used in experiments involving the charging and discharging of capacitors, as well as other transient current studies.
Ballistic Galvanometers (100 or 500 Ohm) typically have a resistance value, which influences their sensitivity and the range of measurements. These devices are often used in applications that require high accuracy over short time intervals.
Exceptional Sensitivity and Precision
This ballistic galvanometer is engineered for high sensitivity, with deflection directly proportional to the charge (micro-coulombs scale). The anti-parallax mirror scale, fine graduations, and knife-edge pointer enable accurate readings. The mirror and lamp arrangement further enhances measurement precision by minimizing reading errors, making it perfect for advanced physics experiments and educational demonstrations.
Robust and User-Friendly Construction
Encased in a durable enamel-coated cast iron body with a non-magnetic frame and glass front, this galvanometer provides long-lasting serviceability. Brass terminals with knurled nuts ensure secure connections, while the zero adjuster and external power source input allow for manual operation and fine-tuning. All relevant accessories and a detailed operation manual are included for straightforward setup and use.
FAQ's of BALLISTIC GALVANOMETER By Labcare Export:
Q: How does the BALLISTIC GALVANOMETER by Labcare Export measure the quantity of electric charge?
A: The galvanometer operates on Faraday's Law of Electromagnetic Induction, generating a proportional deflection on the scale when a charge passes through its moving coil. The ballistic mode records the rapid movement (or 'ballist') caused by a brief current pulse during charge or discharge.Q: What process should be followed to use the galvanometer in a laboratory experiment?
A: Ensure the instrument is properly leveled on a stable surface. Connect your experimental setup using the brass terminals. Adjust the zero using the zero adjuster, then conduct your discharge or charge experiment. Observe the knife-edge pointer reflection on the anti-parallax mirror scale, and record the maximum deflection to determine the quantity of charge.Q: Where is this galvanometer typically used and for what kind of applications?
A: It is commonly used in physics labs, educational institutions, and research settings for experiments involving measurement of electric charge-such as capacitor discharge studies, demonstration of electromagnetic induction, and verification of Faraday's law.Q: When should the quartz fiber or phosphor bronze ribbon suspension be chosen?
A: Both types are supplied to optimize the suspension system's thermal and mechanical properties. Quartz fiber is highly stable and less affected by humidity, suitable for precise, long-term measurements, whereas phosphor bronze is known for durability in general laboratory use.Q: What are the benefits of the mirror scale and anti-static features?
A: The mirror scale eliminates parallax error by allowing you to align the pointer reflection precisely with the scale marking. The anti-static pointer reduces the influence of stray static charges, resulting in more stable, reproducible readings.Q: How does the damping mechanism work and why is it important?
A: The instrument uses air damping with a soft iron cylinder and/or magnetic damping to gently slow the moving coil, preventing overshooting or oscillations. This ensures the pointer settles quickly and accurately at its maximum deflection, providing clear, reliable measurements.Q: What voltage and measurement range can this galvanometer handle?
A: Designed for low-voltage, direct current situations, the galvanometer operates effectively at millivolt ranges and is ideal for measuring charge quantities from 10 micro-coulombs to 200 micro-coulombs, depending on the configuration and experiment setup.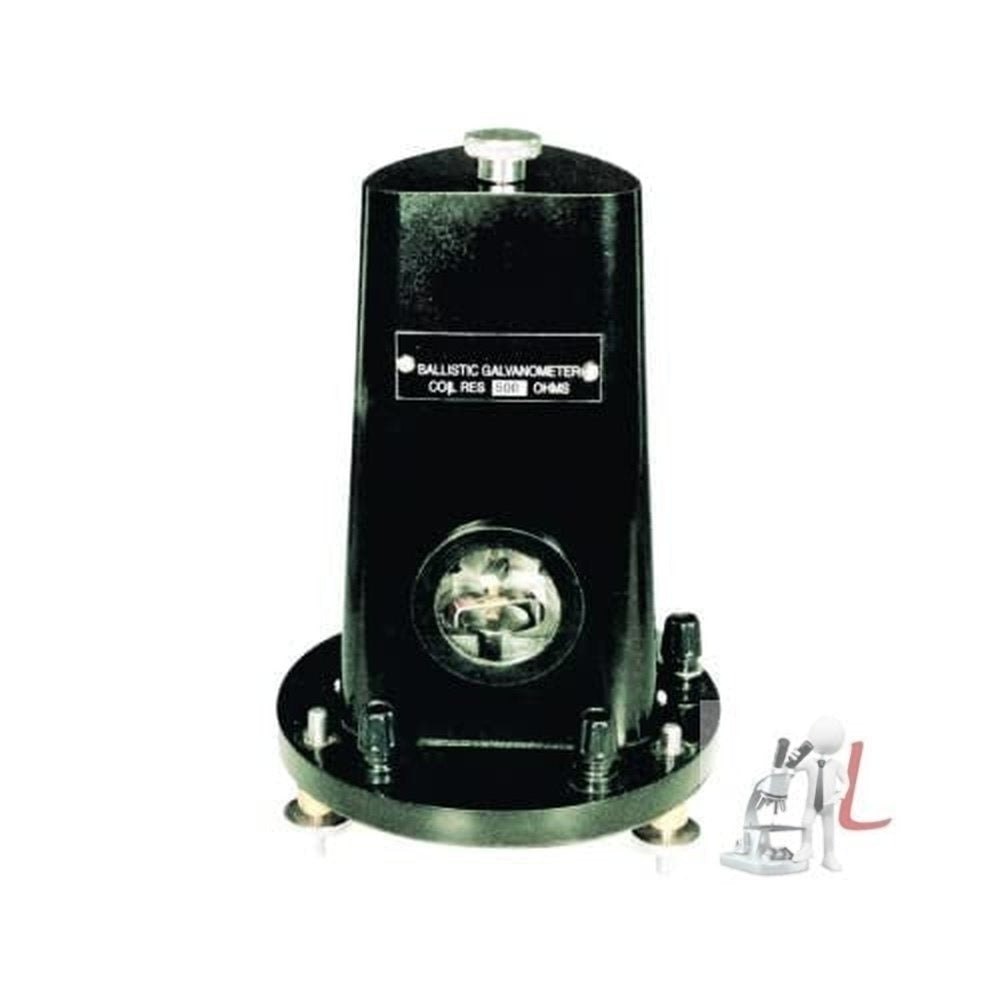

Price:
- 50
- 100
- 200
- 250
- 500
- 1000+
More Products in SCIENCE LAB EQUIPMENT Category
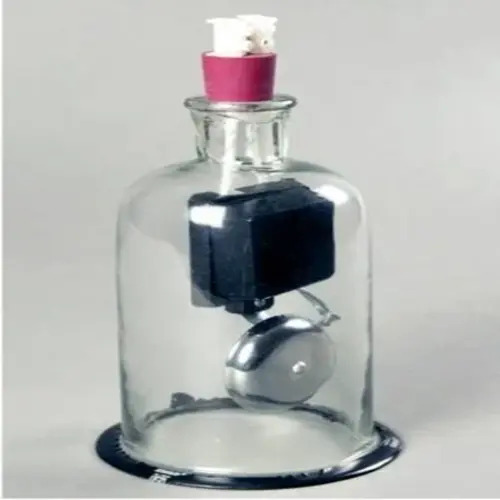
BELL EXPERIMENT APPARATUS By Labcare
Price 850.0 INR / Piece
Minimum Order Quantity : 1 Piece
Power Source : Electric (230V AC)
Dimension (L*W*H) : 32 x 22 x 25 cm
Type : Physics Laboratory Equipment
Display Type : Analog
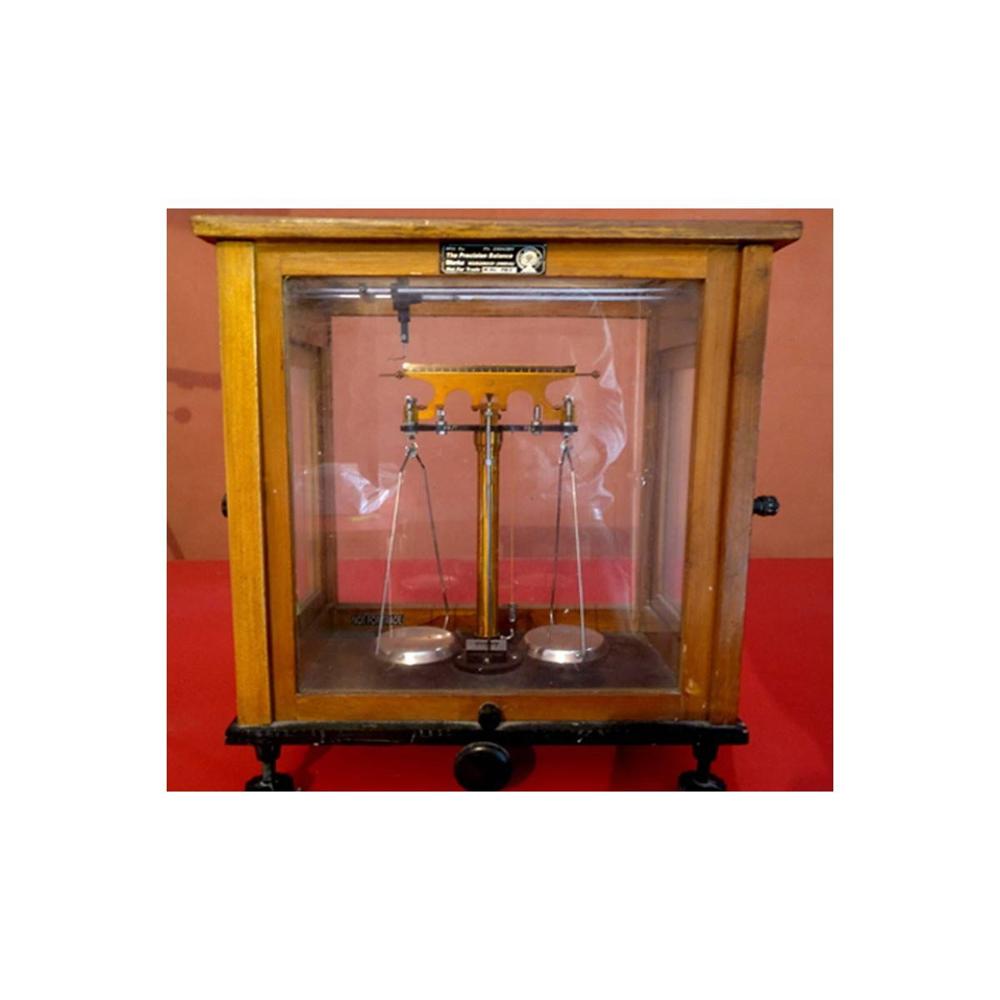
BALANCE PHYSICAL (Cap 250Gm) By Labcare Export
Price 2000.0 INR / Piece
Minimum Order Quantity : 1 Piece
Power Source : Not required (manual)
Dimension (L*W*H) : Approx 300 x 120 x 145 mm
Type : Physical Balance
Display Type : Analog
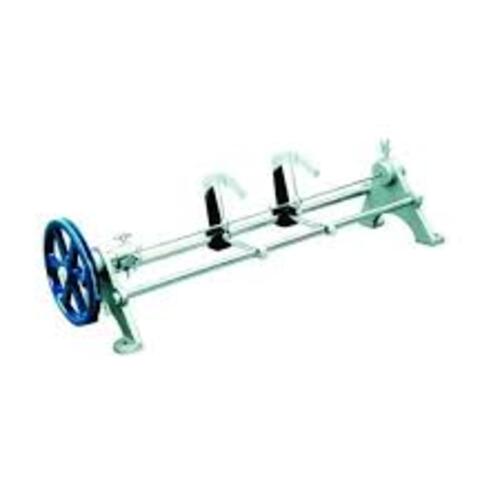
BARTON VERTICAL APPARATUS By Labcare Export
Price 9000.0 INR / Piece
Minimum Order Quantity : 1 Piece
Power Source : Not Required / Manual
Dimension (L*W*H) : 450 x 280 x 600 mm
Type : Vertical Apparatus
Display Type : Analog
ANEROID BAROMETER (by Labcare)
Price 780.0 INR / Piece
Minimum Order Quantity : 1 Piece
Power Source : Not Required (Manual)
Dimension (L*W*H) : Approx. 135mm (Diameter) x 45mm (Thickness)
Type : Aneroid Barometer
Display Type : Analog (Circular Dial)

 Send Inquiry
Send Inquiry





 Send Inquiry
Send Inquiry Send SMS
Send SMS